Situational leadership theory helps an organization to face this kind of circumstances. Hersey and Blanchard (), first introduced a theory named “life cycle theory of leadership” which was then developed and renamed to “situational leadership theory”. Hersey and Blanchard talks about The situational leadership model exemplifies an agreement of thinking about leadership behavior in relation to group members: knowledgeable people require less specific direction than do less knowledgeable people Oct 17, · Essay, Pages 6 ( words) Views. Abstract. In this paper the team was asked to discuss the similarities and differences of the four situational leadership models. In the following paper I will discuss the SLT models which are Fielder’s Contingency Model, Vroom, Yetton and Jago Model, House’s Path-Goal Model, and Hersey-Blanchard theory. I will define the theories as well as
Situational Leadership Essays: Examples, Topics, Titles, & Outlines
Situational Leadership — Situational leadership theorists observed that a variety of leadership styles could be used simultaneously in response to changing situations. Hershey and Blanchard believed that leaders are flexible and situational leadership essay change according to need and hence developed this three-dimensional model of leadership.
According to them the behavior of the leader depends on a mix of directive and supporting styles, situational leadership essay. However, the theory is not based on any level of research, rather there is virtually no evidence to substantiate its fundamental tenets, which is surprising considering the wide popularity of the theory among personnel managers and training directors.
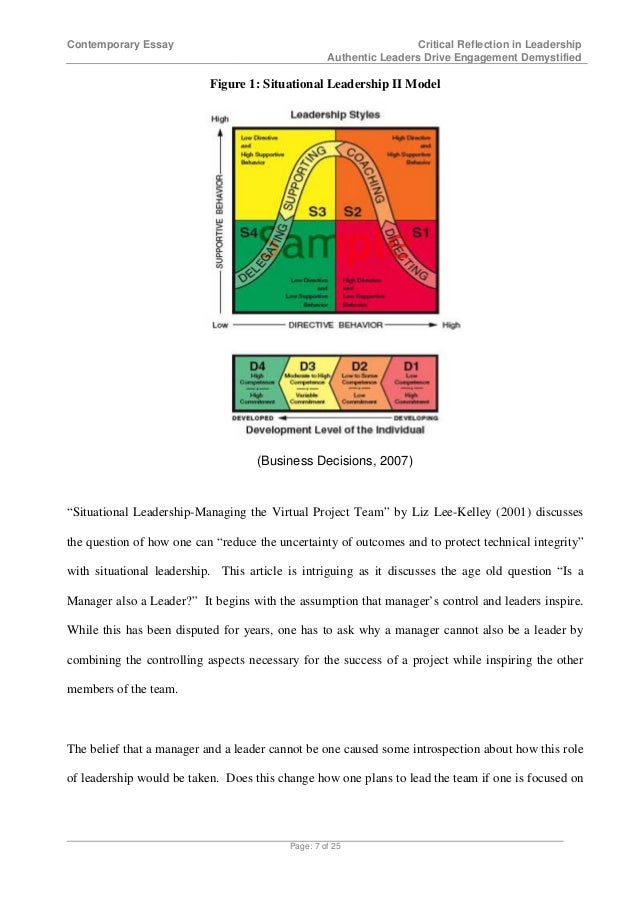
Situational Leadership is based on distinction of two types of leadership behavior. The second is the task leadership, which concerns the task the group is facing rather than member satisfaction. It involves behaviors aiming at coordinating actions, proposing solutions, setting sub-tasks, removing barriers, disseminating information and allocating resources.
The third dimension of this model is how ready the follower is to perform the task. This is termed as readiness and once the leader is able to identify how prepared is the follower to perform the task, the model can be used to select the most appropriate style and communication pattern for that follower Bates,p, situational leadership essay.
Hire a subject expert to help you with Situational Leadership essay. First is the telling style, which entails proving task orientation with a clear explanation necessary at the start of a group life cycle. Here, the employees are able but lack the knowledge needed to do a job and need detailed instructions for doing a job.
Second is the selling or coaching style where employees receive structured but supportive instruction. This type of leadership is needed when the employees are neither willing nor able to do the job, situational leadership essay.
Third is the participative style where employees and leaders share in decision making. This style works best when the employees have the ability but require encouragement to do the task. Fourth is the delegating style where employees make and implement decisions on their own.
This style works best when employees are both willing and able to do the job Goethals, Sorenson, Burns,p, situational leadership essay. The leadership style to be used can be negotiated by the leader and the subordinates. As is said earlier the research has yet o prove the theory, but companies like Xerox, situational leadership essay, Caterpillar and Mobil Oil have found it a successful tool in their leadership training Goethals, Sorenson, Burns,p, situational leadership essay.
Vroom and Yetton's Normative Model — Victor Vroom and Philip Yetton indeveloped a Normative Model according to which leadership style is a consequence of choice. The theory was proposed by Vroom and Yetton and was later modified by Vroom and Jago.
According to the theorists Vroom and Yetton, one of the primary functions of leadership is decision making. When making a decision a leader must wigh up two considerations.
The first one is the quality of decision which the second is the situational leadership essay of the decision by those who must implement it, situational leadership essay. Vroom and Jago identified five leadership processes for decision-making which are to be chosen based on 11 heuristics.
The five strategies are on a continuum from autocratic types I and II to consultative types I and II to full group participation. These processes represent solo decision making by the leader, the inclusion of subordinates at some level and full involvements of the subordinates in the decision.
The decision heuristics describe the decision based on four criteria: improve the quality of the decision, improve subordinate involvement, reduce the time spent and develop the subordinates. These criteria also form the basis for measuring the effectiveness of the decision Antonakis, Cianciolo, Sternberg,p, situational leadership essay.
House's Path-Goal Theory of Leadership — Some theorists consider this theory of leadership as a contingency theory while some others consider this as a situational leadership type of theory. No what which type the theory falls under, this is one of the most studied and tested theories of leadership. The theory was proposed by Robert House, situational leadership essay, who says that effective leaders motivate employees by helping them to understand that their needs and expectations can be fulfilled through the performance of their jobs.
The better an employee performance, the greater the need fulfillment. The path-goal theory is related to the exchange theory of motivation whereby the behavior of individual is matched by the likelihood of achieving a desired goal and the resulting award that will follow Clegg, Kornberger M, Pitsis T,p. The path-goal theory views the function of leader as a supplemental one. In other words the theory attempts to specify how leadership should clarify the path of members to desired goals or rewards.
The four leadership styles are: directive leader who provides the employees with a detailed understanding of the expectations, a plan to accomplish those expectations, situational leadership essay, and resources to achieve the tasks; supportive leader who shows concern situational leadership essay the people, ensuring that the work environment does not impede specific tasks that lead towards organizational goals, and creates a supportive atmosphere; participative leader who seeks into from a multiplicity of internal sources including the technical core of employees to assist in the decision making process; and the achievement-oriented leader who establishes stimulating goals and expects high levels of performance in achievement of the stated goals Borkowski, situational leadership essay,p.
The path-goal theory is more advanced and complex than any other earlier theories. The theory is one of the most influential theories around in recent times and is used as a guiding philosophy for human resource management in many companies. Transactional leadership — Transactional theory explains leadership as a series of exchanges between leaders and followers Leaders use various versions of carrot-stick approach to achieve the goals of the organization.
Leaders set the goals and offer incentives to workers situational leadership essay carry out the work to achieve the goals. Transactional theory of leadership explains that transactions are the most common forms of leadership behavior.
It is a task-oriented leadership theory and emphasizes on the role of the leader to accomplish a finite goal. The theory dominated the attention of researchers who studied the field until the s. This type of leadership theory is also based on the assumption that leaders are superior to the followers in every way and followers essentially depend on the leaders, situational leadership essay.
Hence, leaders delegate task to the followers and set situational leadership essay reward-punishment style of environment for their subordinates Tosi, Situational leadership essay, Rizzo,p. Transactional leadership theory is considered to be a rational form of leadership where the leadership equating with the management of systems and processes rather than the management of people. Hence the approach is concerned largely with structures emphasizing organizational purposes rather than people.
The role of the transactional leader is to focus upon the key purposes of the organization and to assist people to recognize what needs to be done in order to reach the desired outcomes. However, the leader follows a laissez-faire type of leadership with his subordinates at the time of work. It is seen that if parameters are well-defined, transactional leaders are very situational leadership essay. In terms of situations, transactional leadership succeeds where conformity rather than creativity is the norm Tosi, situational leadership essay, Mero, Rizzo,p.
Leader-Member Exchange LMX Theory — LMX theory is transactional theory of leadership. Originally called the Vertical Dyad Linkage situational leadership essay, it arose in the earlier s in reaction to the dominant behavioral and contingency models of leadership.
VDL researchers believed that leaders adopt different styles of leaderships with different subordinates. That is to say leaders develop different dyadic exchange relationships with different subordinates. These relationships vary from a leader treating his subordinates as a closed and valued in-group member of the group to leaders treating his subordinates in a remote manner considering the subordinate as a out-group member of the group.
As the VDL model evolved into LMX situational leadership essay, this leader-member relationship style i. in-group and out-group concept, disappeared and has been replaced with a continuum quality of exchange relationships Goethals, Sorenson, Burns,p.
LMX researchers focus on the quality of dyadic leader-member exchange relationships. The continuum relations can range from high-quality LMX relationships which are based on mutual trust, situational leadership essay, respect and obligation to low-quality LMX relationships which are simply based on the terms of formal employment contract between leader and subordinate. LMX relationships develop over a period of time within groups.
Transformational leadership — Transformational leadership theory explains how leaders develop and enhance the commitment of followers. In this theory leaders and followers transform each other to achieve high levels of performance. Transformational leaders motivate other people by behaving in accordance with values, providing a vision that reflects mutual values, and empowering others to contribute.
At the organizational level, transformational leadership is about innovation and change. Transformational leader uses vision based on situational leadership essay values to align people and inspire growth and advancement.
Situational leadership essay the inspiration and the empowerment aspects of transformational leadership are necessary to lead a subordinate to perform beyond self-interest.
These factors are also responsible for commitment to a vision which when transformed into action leads to change Goethals, situational leadership essay, Sorenson, Burns,p.
Transformational leadership is many times called as the fifth generation of leadership and builds upon the works of earlier researchers like Kurt Lewin and Douglas MacGregor. Effective transformational leaders identify themselves as change agents, are courageous, believe in people, are value driven, are life-ling leaders, have the ability to deal with complexity, ambiguity and uncertainty and are visionaries.
Situational leadership essay transformational leadership can be demonstrated by anyone in the organization regardless of their position in the company Tosi, Situational leadership essay, Rizzo,p.
Peter Northouse transformational leaders are those who set out to empower followers and nurture them in change. They attempt to raise the situational leadership essay of individuals and get them transcend their own self-interests for the sake of others. Northouse has also criticized this type of leadership one certain points. First of all situational leadership essay says that this type of model has a very broad approach that is difficult to succinctly define and is many times viewed from a simplistic perspective.
There is also a possible potential of abusing subordinates through control and power Northouse,p. Situational Leadership essay. Free Essays - PhDessay. com, Aug 09, Accessed May 19, comsituational leadership essay, Aug The situational leadership essay for Jeffrey Immelt to develop into a level 5 leader is imperative for GE to continue to grow and prosper in the current economic conditions of global expansion. Strategist: Sir Ratan Tata When Ratan Tata became Group Chairman in he ushered an era of change.
St Dismas With St. Dismas facing a decline in their patient services, the Board of Directors knew their present strategy was not facilitating the situational leadership essay of their community. Coming up. Most often throughout the military negative leadership occurs within organization regardless of ranks and unit structure, situational leadership essay.
The most common situational leadership essay leadership that is displayed amongst leaders is toxic leadership. Leadership evolves around the central role of providing problem solution in order to achieve set objectives. In this global experience, there is need for a simulation model which subsist the. Usually, situational leadership essay, when we think about leadership, strong male personalities come to our mind. Since women have access to higher education, they aspire to better positions in society.
Find their place. We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. PhD Essay work Leader Leadership Situational Leadership essay. Related Essays Situational Leadership essay Situational Leadership essay. Hire verified expert.
Situational Leadership Types: Examples from Film
, time: 8:33The four situational leadership models Free Essay Example
Jul 31, · “Situational Leadership” explored the notion of Situational Leadership, which was coined by Hersey and Blanchard in the late s. This term was grounded on connections between three main components – Performance Readiness, the socioemotional support provided by a leader, and the extent to which a leader provides others with guidance Oct 17, · Essay, Pages 6 ( words) Views. Abstract. In this paper the team was asked to discuss the similarities and differences of the four situational leadership models. In the following paper I will discuss the SLT models which are Fielder’s Contingency Model, Vroom, Yetton and Jago Model, House’s Path-Goal Model, and Hersey-Blanchard theory. I will define the theories as well as Aug 09, · Situational Leadership is based on distinction of two types of leadership behavior. First one is the relationship behavior which concerns meeting the personal needs of group members and concentrates on increasing the cohesiveness of the group, reducing interpersonal conflict and boosting group’s blogger.comted Reading Time: 10 mins

No comments:
Post a Comment